hydro power

“Hydro” means “water” in Latin – so “hydro power” is made from water.
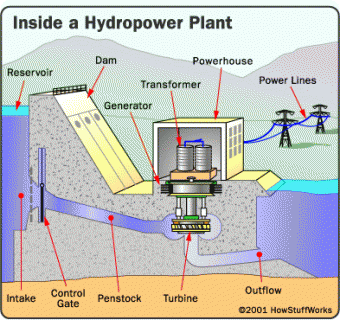
It might sound odd that we can use water to make electricity - they're a dangerous combination, right? Actually, the water never comes in contact with the electricity. The water flowing down a river is used to spin the turbines inside the generator.
People have used water power for more than 2,000 years. Ancient Egyptians used water wheels for grinding grain, and early Americans learned how to use them for sawing wood.
In the 1880s, scientists learned how to use a flowing river to spin the turbines of a generator. The first hydroelectric power plant in the U.S. opened on the Fox River near Appleton, Wisconsin, in 1882.
By the 1940s, nearly half of the electricity in the United States came from hydro power. After World War II, coal power plants became more popular.
Hydro power isn't very common in the Midwest because most of our rivers are small and slow. Alliant Energy has three hydro power plants, including one in Kilbourne, Wisconsin, that's been making electricity for more than 90 years!
Most of the big hydroelectric power plants in the United States are in California, Oregon and Washington.
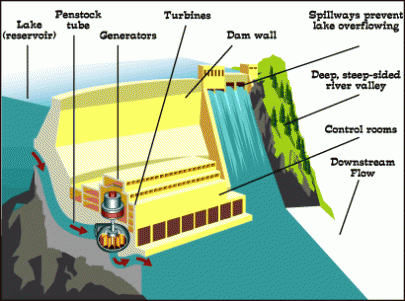
People built dams to control the power of the big mountain rivers. Workers can change the amount of water flowing through the dam depending on the weather and how much electricity people need.
The biggest hydroelectric dam in the United States is the Grand Coulee Dam in Washington. Started in 1933 and completed in 1942, it’s the largest concrete structure ever built: 5,233 feet long and 550 feet high!
It has four power plants with 33 generators, making enough electricity for more than two million homes.
Hydro Power Pros and Cons:
PROS:
~Dams can store rain water or water directly from the river itself. Then, in case of a Drought, the dam will still have a relatively constant supply of water.
~Producing Power.
~Controls flooding & provides recreational activities such as boating fishing and swimming, if the lake is not being used for drinking water (Dam Society).
~Simple design makes for inexpensive repairs and maintenance costs (Dam Society).
~Produce inexpensive (after completion) and clean power. Renewable energy source, because the water is not destroyed by passing through the dam.
~If needed, dams can be shut down instantly, where thermal plants take hours, and nuclear plants can take days! (Dam Society).
~Very few breakdowns.
CONS:
~Hydroelectric power production require flooding of entire valleys and scenic areas.
~Disrupts natural seasonal changes in he river, and ecosystems can be destroyed.
~Ends flooding that help to clean out the silt in rivers, causing them to clog (Energy Laboratory).
~The silt that usually flows down to the Beaches and Estuaries is block by the dam.
~Studies show that the plant decay caused downstream of major dams produces as many greenhouse gasses as more conventional methods of producing electricity.
~Dams are expensive to build, and due to drought may become useless, or produce much less power than originally planned.
~A dam being build in Quebec will end up flooding an area as large as Switzerland (Energy Laboratory). Dams can break in a massive flash flood.